Healthcare IT
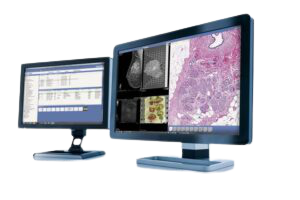
- Radiology PACS Systems
- picture archiving and communication system (PACS) is a medical imaging technology which provides economical storage and convenient access to images from multiple modalities (source machine types Electronic images and reports are transmitted digitally via PACS; this eliminates the need to manually file, retrieve, or transport film jackets, the folders used to store and protect X-ray film. The universal standard format for PACS image storage and transfer is DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine). Non-image data, such as scanned documents, may be incorporated using consumer industry standard formats like PDF (Portable Document Format), once encapsulated in DICOM. A PACS consists of four major components: The imaging modalities such as X-ray plain film (PF), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a secured network for the transmission of patient information, workstations for interpreting and reviewing images, and archives for the storage and retrieval of images and reports. Combined with available and emerging web technology, PACS has the ability to deliver timely and efficient access to images, interpretations, and related data. PACS reduces the physical and time barriers associated with traditional film-based image retrieval, distribution, and display

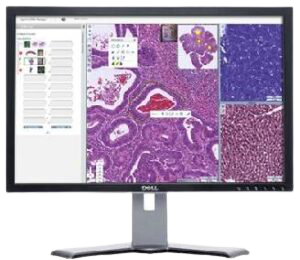
Pathology PACS Systems
- Digital Pathology Solution helps you make quick and accurate diagnoses of histopathology and cytology cases. The high-end digital review application gives you the right tools to perform daily tasks and reduce the pain points you get with time-consuming manual workflow. This includes sorting of images, use of built-in or integrated image analysis, and built-in reporting module—to mention a few examples. Full case overview—including images from different scanners with different file formats, macro cameras, and other image systems—as well as patient data from information systems in the same application.
Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
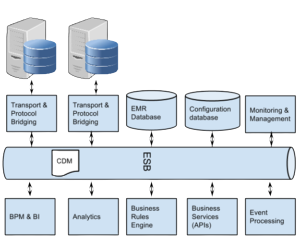
- is an element of health informatics that focuses mainly on the administrational needs of hospitals. In many implementations, an HIS is a comprehensive, integrated information system designed to manage all the aspects of a hospital’s operation, such as medical, administrative, financial, and legal issues and the corresponding processing of services. Hospital information system is also known as hospital management software (HMS) or hospital management system. Hospital information systems provide a common source of information about a patient’s health history. The system has to keep data in a secure place and controls who can reach the data in certain circumstances. These systems enhance the ability of health care professionals to coordinate care by providing a patient’s health information and visit history at the place and time that it is needed. Patient’s laboratory test information also includes visual results such as X-ray, which may be reachable by professionals. HIS provide internal and external communication among health care providers. Portable devices such as smartphones and tablet computers may be used at the bedside. Hospital information systems are often composed of one or several software components with specialty-specific extensions, as well as of a large variety of sub-systems in medical specialties from a multi-vendor market. Specialized implementations name for example laboratory information system (LIS), Policy and Procedure Management System, radiology information system (RIS) or picture archiving and communication system (PACS).

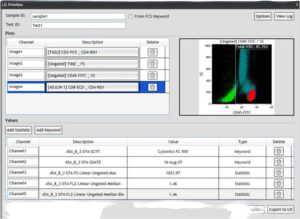
CLINICAL Lab INFORMATION MANAGEMENT TOOLS
- clinical information management tools provide: Centralized management of laboratory instrumentation and data workflows to deliver high quality test results with short turnaround time . Real-time operational analysis to support clinical and business decision-making . Laboratory efficiency delivered through standardization, improved workflow and automated notifications .Scalable infrastructure to minimize redundant capital investment and recurring costs across the care delivery network

Patient Monitoring IT
- vision for the future of critical care and what’s on the horizon for connected technologies in the hospital Medical technologies that communicate in a secure and standardized way .Bidirectional communications between medical devices and EMR systems data connectivity that improves efficiency and safety, optimizes clinical outcomes, and reduces costs

.
.
.
.
.
.
